Complete guide to obtaining and using a National Tax Number (NTN) in Pakistan. Learn about the application process, required documents, tax compliance, and more.
National Tax Number (NTN)
The National Tax Number (NTN) is a pivotal tool in Pakistan’s tax system, ensuring transparency, efficiency, and legal compliance in the economic activities of individuals and businesses. Issued by the Federal Board of Revenue (FBR), it is required for all entities participating in taxable transactions, and it plays a key role in fostering good governance and tax compliance.
What is NTN?
The National Tax Number (NTN) is a unique identification number assigned by the Federal Board of Revenue (FBR) to individuals, businesses, and other entities. It serves as a means to track and monitor tax compliance, ensuring that taxpayers meet their obligations under Pakistan’s tax laws. The NTN is required for various tax-related activities, including income tax, sales tax, and federal excise duty compliance.
Key Features:
- Unique Identifier: The NTN helps the FBR monitor tax compliance by assigning a unique number to every taxpayer.
- Filing of Tax Returns: It is essential for submitting tax returns and processing business transactions.
- Business Operations: NTN is required for business registration, and is crucial for entities engaged in trade, import/export, and government procurement.
- Transparency: It facilitates the creation of a formal, regulated economic environment by linking businesses and individuals to the tax system.
Who Needs an NTN?
An NTN is essential for compliance with Pakistan’s tax laws and is required for various business, financial, and regulatory activities. Here’s a detailed breakdown of who needs an NTN in Pakistan:
Individuals
- Salaried Employees: Individuals earning taxable income above the threshold set by the tax laws.
- Freelancers and Consultants: Professionals such as doctors, lawyers, engineers, designers, and other self-employed individuals with taxable income.
- Business Owners and Traders: Individuals engaged in business activities, including sole proprietors.
- Non-resident Pakistanis: Those with income from sources in Pakistan or engaging in business activities.
Businesses
- Sole Proprietors: Individuals operating a business under a registered name.
- Partnerships and Associations of Persons (AOPs): Partnerships or organizations formed by two or more individuals for business purposes.
- Companies:
- Private Limited Companies
- Public Limited Companies
- Single Member Companies
- Retailers, Wholesalers, and Manufacturers: Businesses involved in commercial sales or production.
- Freight Forwarders & Importers/Exporters: Entities involved in international trade need NTN for customs registration.
Non-Profit Organizations (NPOs)
- NGOs, Trusts, and Charities: Organizations seeking tax exemptions or grants from government agencies.
- Social Welfare Entities: Non-profit entities engaged in charitable work or public welfare activities.
Other Entities
- Educational Institutions, Hospitals, and other service providers involved in taxable activities.
Importance of NTN
The National Tax Number (NTN) plays a crucial role in Pakistan’s tax system and offers several key benefits for both individuals and businesses. Here’s a breakdown of its importance:
Legal Compliance
- Tax Filing: NTN is mandatory for filing income tax, sales tax, and federal excise duty returns under Pakistan’s tax laws, ensuring taxpayers fulfill their legal obligations.
- Income Tax Ordinance Compliance: It ensures adherence to the Income Tax Ordinance, 2001, which is the primary law governing tax compliance in Pakistan.
Business Operations
- Opening a Business Bank Account: Businesses need an NTN to open corporate bank accounts, facilitating financial transactions.
- Import/Export Activities: NTN is required to register with the Web-Based One Customs (WEBOC) system for customs clearance, essential for conducting international trade.
- Government Tenders and Contracts: Many government tenders and contracts require NTN for participation, making it essential for businesses to engage in public sector projects.
Tax Benefits
- Tax Refunds: NTN holders are eligible to claim tax refunds, reducing their financial burden.
- Lower Withholding Tax Rates: Non-filers face higher withholding tax deductions. Having an NTN and filing taxes helps individuals and businesses benefit from lower tax rates.
- Access to Tax Exemptions: Certain entities, such as NGOs, may qualify for tax exemptions with a valid NTN.
Financial Transparency
- Ensures Traceability: NTN provides transparency by linking individuals and businesses to their financial activities, ensuring accurate monitoring of income and expenditures.
- Helps Prevent Tax Evasion: By assigning a unique identification number, NTN helps the Federal Board of Revenue (FBR) trace and prevent tax evasion or non-compliance.
Facilitates Import/Export
- Customs Registration: NTN is essential for registering with customs authorities for smooth import and export operations.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensures that businesses comply with the regulations governing cross-border trade.
Participation in Formal Economy
- Encourages Formalization: The NTN helps bring businesses into the formal economy, contributing to national economic development and creating a tax-compliant culture.
- Access to Financial Services: NTN holders have better access to loans, credit, and other financial services as banks and financial institutions use NTN for KYC (Know Your Customer) purposes.
In summary, the NTN is integral for ensuring legal compliance, securing business operations, availing tax benefits, and fostering transparency in Pakistan’s financial and economic activities. It simplifies the process for businesses and individuals to operate within the formal economy while contributing to the country’s tax system.
How to Apply for NTN?
To apply for a National Tax Number (NTN) in Pakistan, you can follow a simple step-by-step process through the IRIS portal (the FBR’s online system) or manually at a Regional Tax Office (RTO). Here’s a detailed guide on both methods:
Applying Online via IRIS Portal (Preferred Method):
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to get National Tax Number (NTN) online via IRIS 2.0:
Create an Account on IRIS:
Estimated Time: 2-5 minutes.
- Visit the official IRIS 2.0.
- Navigate to the Bottom Right section and select New Registration.
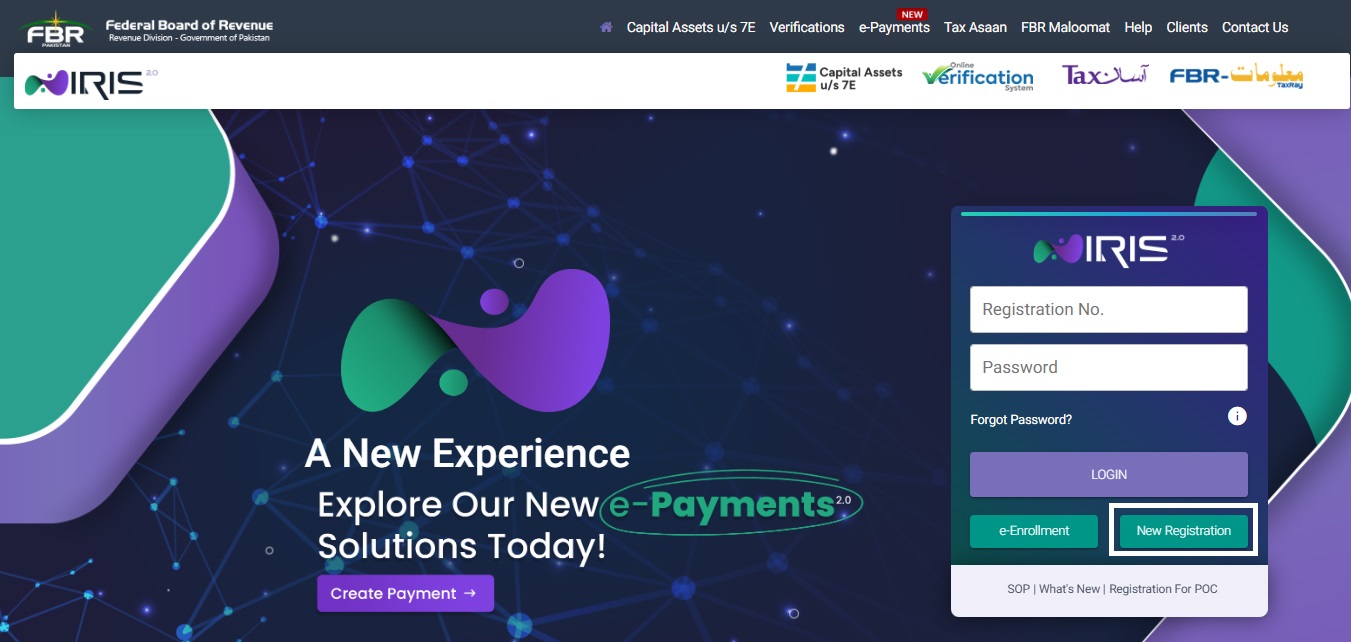
2. Enter Basic Information:
Estimated Time: 3-5 minutes.
- CNIC: Enter your 13-digit CNIC (Computerized National Identity Card) number.
- Prefix: Choose the prefix (Mr./Ms./Mrs.) as per your CNIC.
- Full Name: Provide your first name, middle name, and last name exactly as it appears on your CNIC.
- Current Service Provider: Select your mobile network operator (e.g., Jazz, Telenor, Zong, Ufone).
- Cell Number: Enter the mobile number registered with your service provider.
- Confirm Cell Number: Re-enter your mobile number for verification.
- Email: Provide an active email address for correspondence.
- Confirm Email: Re-enter the email address to confirm it’s correct.
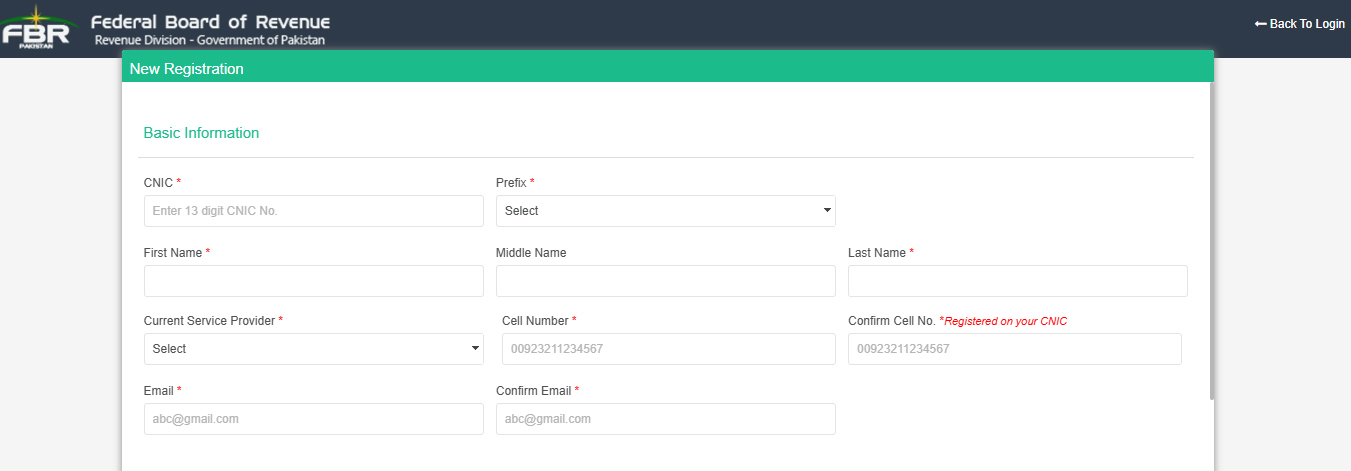
Pro Tips: Use mobile number registered on your CNIC. Email address must be in your reach.
3. Enter Address Information:
Estimated Time: 3-5 minutes.
- Type: Select the address type (e.g., Residential, Commercial).
- Address Form: Choose the format of your address (e.g., House No., Street Name).
- Measurement Unit: Select the unit of measurement (e.g., Marla, Square Feet).
- Total Area: Input the total area of the property in the chosen unit.
- Unit No.: If applicable, enter the unit number.
- Complex/Street Name: Mention the complex or street name where the property is located.
- Area/Locality: Specify the area or locality.
- City: Enter the city of residence.
- District: Select the district from the dropdown list.
- Capacity (if applicable): Select the property capacity, if relevant.
- % Share (if applicable): Mention your share percentage in the property.
Pro Tip: Although you can change your address later, however, change of RTO is a complicated process. Therefore think twice before entering your address details as this will lock your RTO.
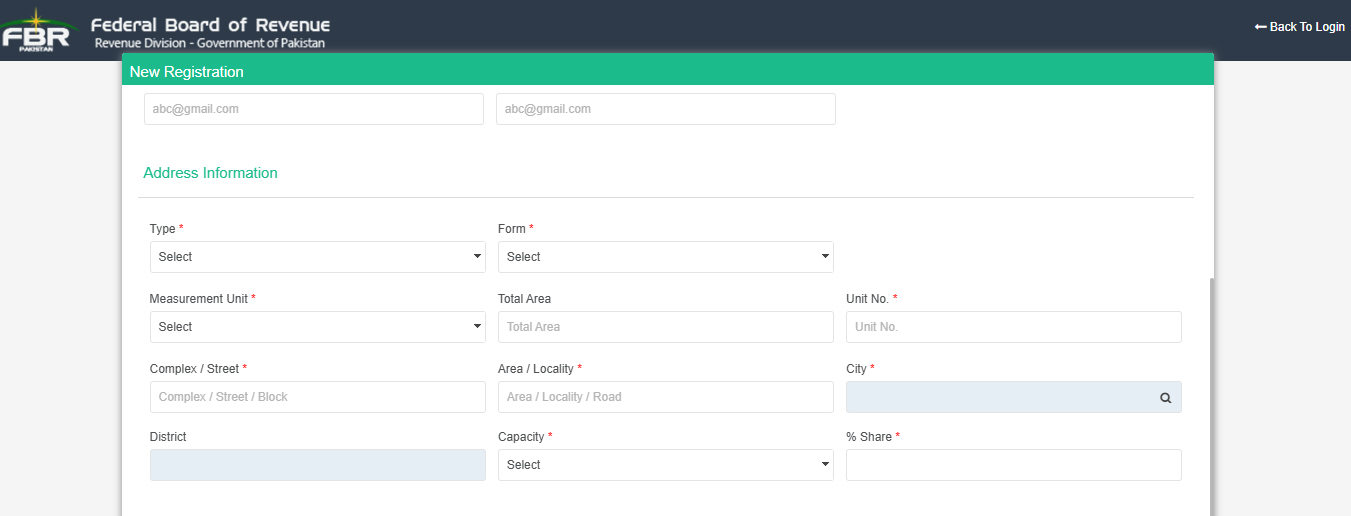
Pro Tip: If you’re a tenant and using one portion of double storey house, enter 50% as shares after selecting Tenant in Capacity.
4. Captcha Verification:
Estimated Time: 1-2 minutes.
- Enter the captcha code shown on the screen to verify you are a human and not a bot.
Pro Tip: FBR Captcha is case-sensitive.
5. Submit the Application:
Estimated Time: 1-2 minutes.
- Double-check all the information entered for accuracy.
- Click the Submit button to submit your NTN registration application.
Pro Tip: Ensure all information is accurate and matches official documents, such as your CNIC.
Manual Process (At Regional Tax Office – RTO):
If you prefer to register National Tax Number (NTN) manually, visit the nearest RTO of the FBR in your region. The FBR representative will review your documents. After successful verification, FBR will issue your NTN.
Verifying Your NTN Online
To verify your National Tax Number (NTN) online through the IRIS 2.0 portal, follow the steps below:
Visit the IRIS 2.0 Portal
-
- Go to the official IRIS 2.0 website (accessible through the FBR portal).

Navigate to Online Verification
-
- Scroll down to find the Online Verification section on the homepage.
- From the left menu, select Taxpayer Profile Inquiry.
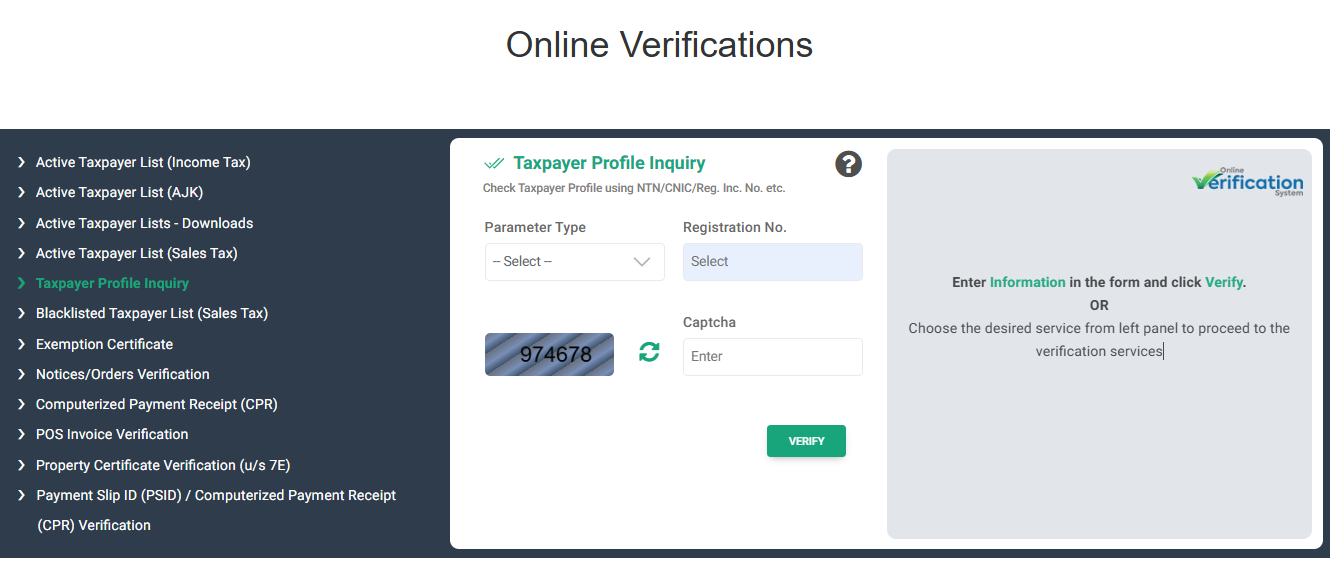
Enter the Required Information:
-
- Select Parameter Type: Choose one of the following options to search:
- NTN (National Tax Number)
- CNIC (Computerized National Identity Card)
- Passport No.
- Registration/Income Tax Number
- Enter Registration No.: Input the value in the Registration No. field, depending on the parameter type selected (e.g., NTN, CNIC, etc.).
- Select Parameter Type: Choose one of the following options to search:
Captcha Verification:
-
- A 6-digit Captcha code will appear on the screen.
- Enter the Captcha code in the provided field to confirm you’re not a bot.
Click Verify:
-
- Click on the Verify button to proceed.
Review Your Taxpayer Profile Inquiry:
Once the verification is complete, the Taxpayer Profile Inquiry page will open. Among the details provided, your NTN will be listed as the Reference No. The page will also display the following information:
-
-
- Registration No.
- Reference No. (This is your NTN)
- Name
- Email Address (will be displayed partially)
- Cell Number (will be displayed partially)
- Address
- Registered On (date of registration)
- Tax Office (Regional Tax Office or RTO)
- Any Business Registered on Taxpayer CNIC
-
Required Documents for NTN Application:
Obligations After Obtaining NTN
After obtaining your National Tax Number (NTN), there are several key obligations and responsibilities that you must fulfill as a taxpayer. Here’s a detailed overview:
Filing Income Tax Returns:
-
- As a taxpayer, you are required to file annual income tax returns with the Federal Board of Revenue (FBR).
- This includes reporting your income, deductions, and any applicable tax liabilities for the year.
- The income tax return must be filed within the deadlines set by the FBR to avoid penalties and fines.
Payment of Taxes:
-
- Based on your income and other tax liabilities, you must pay taxes according to the applicable tax rates.
- Taxes should be paid on time to avoid late fees, interest, and penalties.
- You can make payments through authorized banks or online payment systems provided by the FBR.
Maintaining Proper Records:
-
- You are obligated to maintain accurate records of your income, expenses, receipts, and any other relevant documents for a period of at least six years.
- These records should be available for inspection by the FBR if needed.
Timely Submission of Sales Tax and Other Returns (if applicable):
-
- If your business is registered for Sales Tax, Federal Excise Duty, or any other tax, you must file the relevant returns and make payments on time.
- Ensure compliance with all applicable tax laws and regulations for your specific business activity.
Tax Deduction and Collection:
-
- If you are an employer or involved in certain transactions, you may be required to deduct taxes at source (e.g., for employees’ salaries, contractors, or suppliers) and remit these amounts to the FBR.
- You must issue tax certificates to employees and suppliers showing the tax deducted.
Updating NTN Information:
-
- If there are any changes in your personal or business information (such as a change of address, business details, or marital status), you must update your NTN information with the FBR.
- Failure to update your details may result in fines or penalties for incorrect or outdated information.
Compulsory Audit (if applicable):
-
- In some cases, based on income thresholds or other criteria, you may be subject to a tax audit by the FBR.
- During an audit, you must provide all necessary documentation and cooperate with the tax authorities.
Compliance with Tax Laws and Regulations:
-
- As an NTN holder, it is your responsibility to ensure compliance with all tax laws and regulations set by the FBR.
- Stay informed about any changes in tax rates, filing deadlines, or new tax policies that may affect you.
Engagement in Taxpayer’s Rights and Obligations:
-
- Understand your rights and obligations as a taxpayer, including the ability to challenge any FBR assessments or decisions through the appropriate channels.
- If you believe that your taxes have been overpaid or that you qualify for tax exemptions or refunds, you have the right to apply for adjustments or claims.
Pro Tip: Failure to comply with the above obligations may result in penalties, fines, or legal action by the FBR. It is crucial to stay up to date with all filing requirements and ensure timely payment of taxes.
8. Common Issues and Solutions
Problem: Application Rejection
- Reason: Incorrect or incomplete details.
- Solution: Double-check your information and ensure that all required documents are uploaded correctly.
Problem: Higher Withholding Tax Deduction
- Reason: Non-filer status.
- Solution: File tax returns to be added to the Active Taxpayer List (ATL).
Problem: NTN Verification Issues
- Reason: NTN not linked to your CNIC or business name.
- Solution: Contact the FBR helpline or visit the nearest RTO for assistance.
9. Tips for Compliance
- Engage a Tax Consultant: Professional advice ensures accurate filing and compliance with tax regulations.
- Stay Updated: Monitor changes in tax laws and FBR notifications to avoid inadvertent errors.
- File on Time: Avoid penalties by adhering to filing deadlines.
- Use Technology: Leverage the IRIS portal for efficient tax management and timely updates.
Avoid Common Pitfalls:
- Failing to maintain proper documentation, which may lead to discrepancies during audits.
- Submitting incomplete or inaccurate information in tax returns, risking application rejection or penalties.
- Neglecting to update your contact or business details with FBR, which may cause missed communications or compliance notices.
This guide provides a comprehensive understanding of the NTN process in Pakistan. For more personalized assistance or to address specific queries related to your NTN, feel free to consult a tax consultant or reach out to the FBR.

